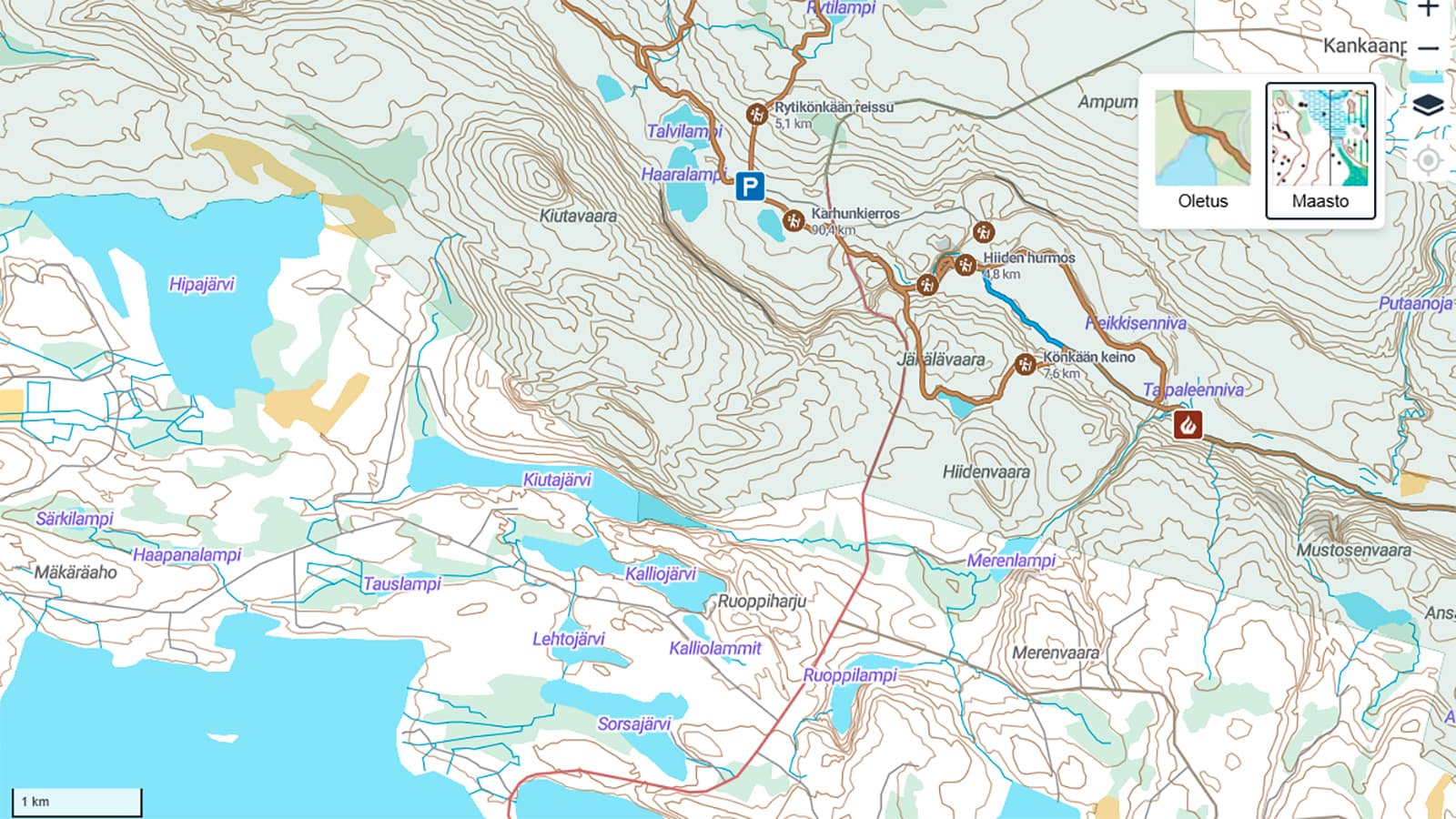
A topographic map is an essential tool for hikers, helping them navigate safely and efficiently in nature. The topographic maps on Luontoon.fi provide detailed information about terrain features, accessibility, and land use. In this article, we go through the basics of reading a topographic map, including common map symbols, colour meanings, contour lines, scale, and access rights.
What does a topographic map show?
A topographic map is a depiction of the terrain viewed from above, using agreed-upon symbols and colours to represent different features of the landscape. The map helps you understand the shapes of the land, bodies of water, vegetation, buildings, and roads. The topographic maps on Luontoon.fi are based on data from the National Land Survey of Finland and are useful for hikers and other outdoor enthusiasts.
Tips for beginners
Reading a topographic map is a skill that improves with practice. Start with easy routes and gradually move on to more challenging terrain. Luontoon.fi provides excellent maps and trail suggestions to support your hiking.
- Practice reading the map: Start by familiarising yourself with the map symbols and colours.
- Plan your route in advance: Take note of the terrain’s features and ease of movement.
- Use a compass: It helps you orient in the right direction.
- Follow the rules: Respect nature and observe area-specific guidelines.
Learn the most common map symbols
Reading a topographic map requires an understanding of map symbols and colours. It’s a good idea to learn at least the most common ones. Map symbols are visual representations of terrain features, such as trails, roads, buildings, powerlines, boulders, and landforms.
You can find more information about map symbols at: suunnistusliitto.fi (in Finnish).
Map colours and their meanings
The colours used on topographic maps help interpret the landscape and plan your route accordingly.
- White (typical forest): These areas are generally easy to walk through as the vegetation is sparse. Trails and routes are clear, and the terrain is flat – ideal for peaceful walks and nature observation.
- Green (dense or difficult forest): Indicates dense forest where movement may be difficult. Darker shades mean thicker vegetation, such as shrubs and undergrowth, which may slow you down. Clear paths may be harder to find in these areas.
- Yellow (open area): Fields and meadows are usually easy to traverse and offer good visibility. Perfect for picnics, birdwatching, and enjoying the scenery – but be prepared for wind and sun exposure.
- Blue (water features): Represents lakes, rivers, and mires. Movement near water can be challenging, especially in mires, which may be wet and soft. Lakeshores and riversides offer beautiful views and opportunities for fishing or swimming – but beware of slippery edges and strong currents.
- Brown (elevation): Shows terrain height differences like hills and valleys. These areas can be physically demanding but offer great views and challenging hikes. Be prepared for steep ascents, descents, and rocky trails.
- Grey (exposed bedrock): Grey areas are bare rock, which can be slippery and require caution. They often offer panoramic views and are popular with climbers. Good footwear and gear are essential.
- Black (man-made structures): Depicts buildings and roads, as well as large boulders. These features can help with navigation and may offer shelter or rest stops.
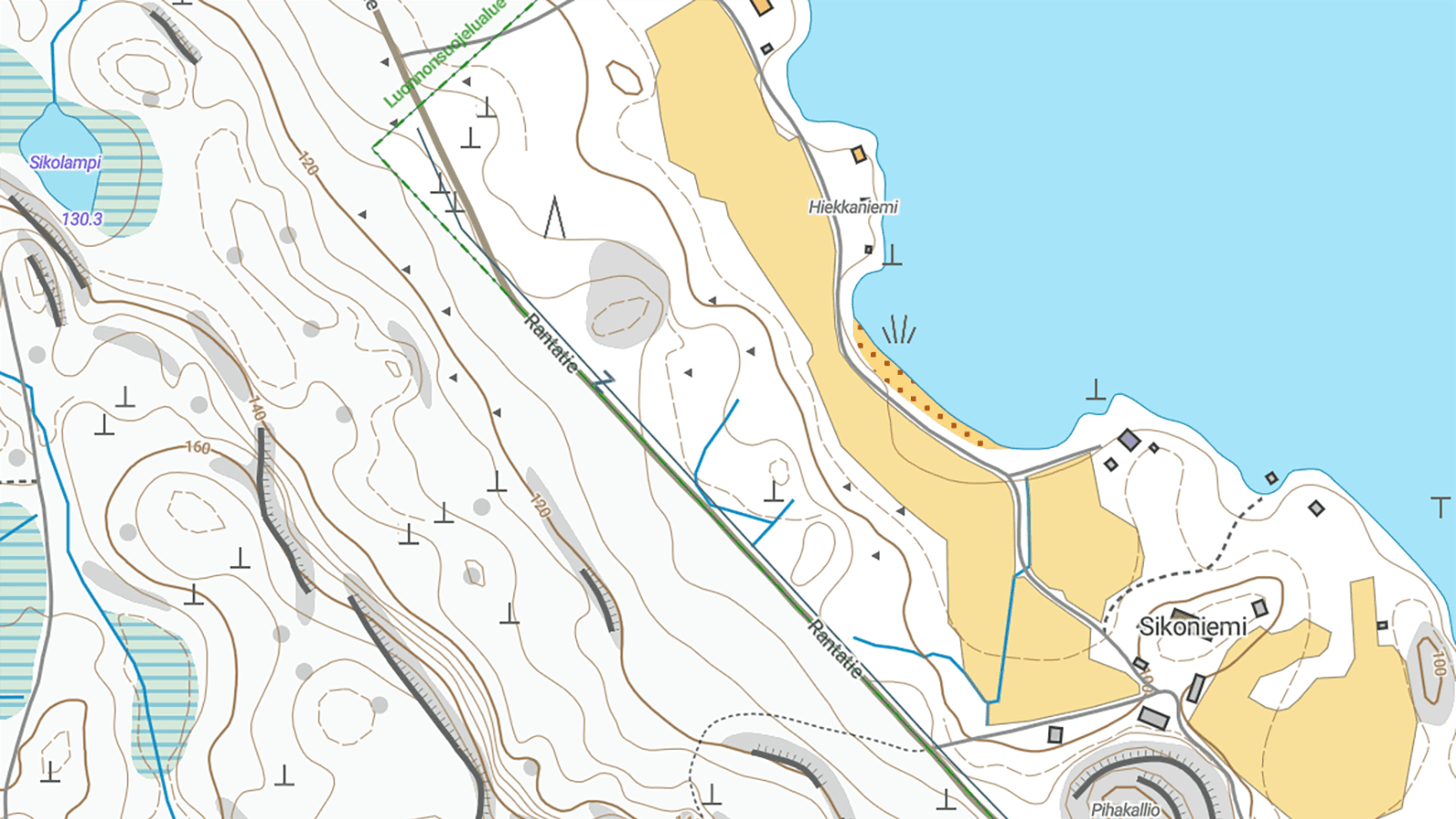
Contour lines reveal the shape of the land
Contour lines are brown lines that show changes in elevation. Each line connects points at the same height above sea level.
- Closely spaced lines: Steep slope.
- Widely spaced lines: Gentle slope or flat terrain.
- Closed loop: Hill or rise.
Use the map scale to measure distances
The map scale helps you estimate distances on the map and translate them to real-world distances. For example, a scale of 1:20,000 means that 1 cm on the map equals 200 metres on the ground.
Where can you go – and where not?
In Finland, everyman's rights allow free movement in nature, but it is important to know the limitations:
- Permitted areas: Forests, trails, roads, and bodies of water.
- Prohibited areas: Cultivated fields, yards, and protected areas with movement restrictions.
- Remember: Everyman's rights do not apply in the same way within protected areas.